Book on Whatsapp
9892101616
Normal TSH Range for Women and What It Means for Your Health
Thyroid
Mon Feb 17 2025
The thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall well-being. Produced by the pituitary gland, TSH stimulates the thyroid to produce hormones that control various bodily functions. Maintaining a normal TSH range is essential for women's health, as fluctuations can lead to issues like fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and fertility problems.
Understanding the Normal TSH Range for Women
The normal TSH range for women varies slightly based on age, pregnancy status, and overall health. However, general guidelines are as follows:
- Non-pregnant adult women: 0.5 – 4.5 mIU/L
- Women planning pregnancy: 0.5 – 2.5 mIU/L (Ideal for conception)
- Pregnant women:
- First trimester: 0.1 – 2.5 mIU/L
- Second trimester: 0.2 – 3.0 mIU/L
- Third trimester: 0.3 – 3.0 mIU/L
- Postmenopausal women: Can be slightly higher but should remain within the normal range.
A TSH level outside these ranges could indicate hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and may require medical attention.
What Abnormal TSH Levels Mean for Your Health
1. High TSH Levels – Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
When TSH levels are above the normal range, it suggests that the thyroid is not producing enough hormones. This condition is more common in women, especially after the age of 40.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism:
- Fatigue and low energy
- Unexplained weight gain
- Hair thinning or hair loss
- Dry skin and brittle nails
- Depression or mood changes
- Slow metabolism and constipation
- Cold intolerance
Possible Causes:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (an autoimmune disorder)
- Iodine deficiency
- Postpartum thyroiditis
- Pituitary gland dysfunction
Health Risks:
- Untreated hypothyroidism can lead to infertility, heart disease, and goiter (thyroid gland enlargement).
2. Low TSH Levels – Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
When TSH levels are below the normal range, it indicates an overactive thyroid producing excessive hormones.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism:
- Rapid weight loss despite normal eating habits
- Increased heart rate and palpitations
- Anxiety, nervousness, or irritability
- Excessive sweating and heat intolerance
- Sleep disturbances
- Weakness and muscle tremors
Possible Causes:
- Graves’ disease (autoimmune hyperthyroidism)
- Thyroid nodules
- Excessive iodine intake
- Overuse of thyroid medications
Health Risks:
- Untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to osteoporosis, heart complications, and thyroid storm (a life-threatening condition).
Importance of TSH Testing for Women
Regular TSH testing is essential for early detection and management of thyroid disorders. It is particularly important for:
- Women planning pregnancy (as thyroid imbalances affect fertility)
- Pregnant women (to prevent complications like miscarriage or preterm birth)
- Postmenopausal women (to monitor changes in metabolism and bone health)
- Women experiencing unexplained weight changes, mood disorders, or fatigue
How to Maintain a Healthy Thyroid
- Balanced Diet: Include iodine-rich foods (seafood, dairy), selenium (nuts, seeds), and zinc (meat, beans) for thyroid support.
- Regular Exercise: Helps maintain metabolism and hormone balance.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can affect thyroid function. Practice yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Regular Thyroid Checkups: Routine blood tests help monitor TSH levels and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Maintaining a normal TSH range is crucial for women’s overall health. Whether you are planning a pregnancy, dealing with weight fluctuations, or experiencing fatigue, regular TSH testing ensures early diagnosis and timely treatment. A well-balanced
lifestyle, along with proper medical guidance, can help keep your thyroid healthy and support long-term well-being.
Related Tests
Related Packages
Related Blogs
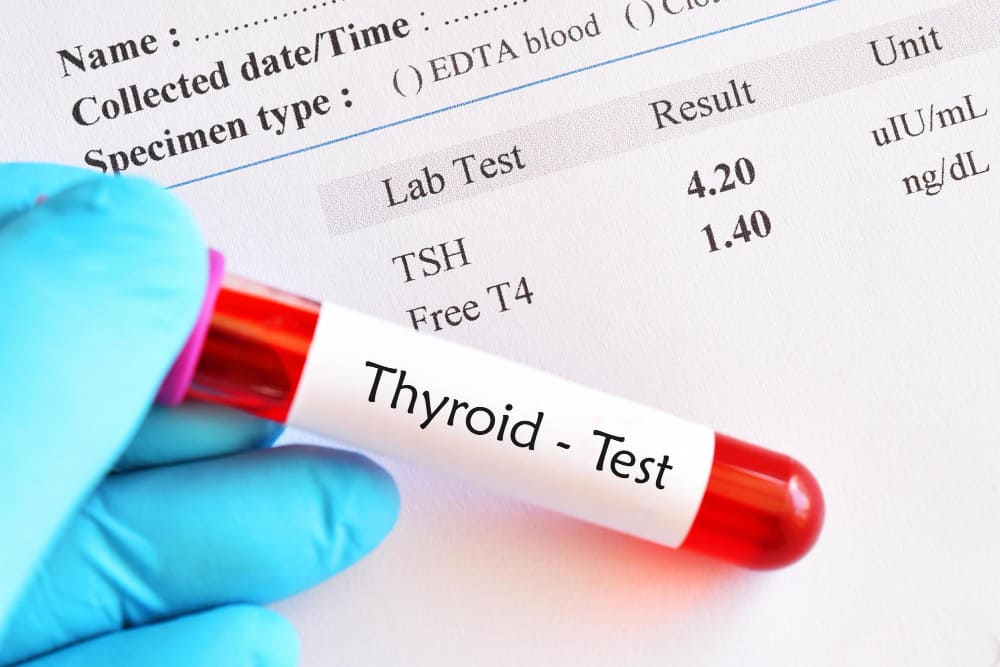
Thyroid
Role of Advanced Diagnostic Tests in Thyroid Cancer Detection
Thyroid cancer is one of the most common endocrine malignancies, and its incidence has been steadily increasing worldwide. Although many thyroid cancers progress slowly, early detection is crucial to ensure effective treatment and improved survival rates. Traditionally, physical examination and basic imaging were the primary methods for identifying thyroid abnormalities. However, with advancements in medical technology, modern diagnostic tests have significantly enhanced the accuracy of thyroid cancer detection. These advanced tools not only help in early diagnosis but also guide treatment decisions and reduce the risk of unnecessary interventions.
Ultrasound Imaging
High-resolution ultrasound is the first-line diagnostic tool for evaluating thyroid nodules. It provides detailed information about the size, shape, and texture of nodules. Features such as irregular margins, microcalcifications, and hypoechogenicity can indicate a higher risk of malignancy. Doppler ultrasound further assists by evaluating blood flow patterns, improving differentiation between benign and malignant nodules.
Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB)
FNAB remains the gold standard for diagnosing thyroid cancer. Under ultrasound guidance, a thin needle is used to collect cells from suspicious nodules. These samples are then examined under a microscope to determine if cancerous changes are present. Although highly reliable, FNAB sometimes yields indeterminate results, which has prompted the development of additional molecular and genetic testing.
Molecular and Genetic Testing
One of the most significant advancements in thyroid cancer detection is the use of molecular diagnostics. Tests that analyze genetic mutations, such as BRAF, RAS, RET/PTC, and PAX8/PPARγ, help improve diagnostic accuracy when FNAB results are inconclusive. Identifying these mutations not only aids in diagnosis but also provides insights into the aggressiveness of the cancer and helps tailor targeted therapies.
Thyroglobulin Testing
Thyroglobulin is a protein produced by the thyroid gland. While it is not used as an initial diagnostic tool, it plays a vital role in monitoring patients after thyroid cancer treatment. Elevated levels of thyroglobulin in patients who have undergone thyroid removal may suggest cancer recurrence.
Radionuclide Scans
Nuclear medicine imaging, particularly using radioactive iodine (I-123 or I-131), is valuable for assessing thyroid function and detecting cancer spread. These scans help determine whether a thyroid nodule is “hot” (overactive and usually benign) or “cold” (underactive and potentially malignant). Post-treatment scans are also essential for monitoring residual thyroid tissue or metastasis.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans
PET scans, often combined with CT, are used in advanced cases where other tests may not clearly detect cancer spread. They are particularly useful in patients with aggressive thyroid cancers or when standard radioactive iodine scans are negative. PET scans provide a whole-body overview, allowing for comprehensive staging of the disease.
The Importance of Early and Accurate Diagnosis
Advancements in diagnostic technology have transformed thyroid cancer management. Early and precise detection ensures patients receive the most suitable treatment—whether surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, or targeted molecular approaches—while avoiding unnecessary interventions in benign cases.
From high-resolution imaging and FNAB to molecular testing and PET-CT scans, these innovations enable doctors to diagnose with greater confidence and tailor treatments for the best outcomes.
Your Partner in Accurate Thyroid Diagnostics – Manipal TRUtest
At Manipal TRUtest Diagnostics, we combine advanced imaging with cutting-edge molecular and pathology testing to ensure precise thyroid cancer detection and monitoring. Our state-of-the-art facilities and expert teams help detect abnormalities early, enabling timely treatment and better recovery outcomes.
Book your Thyroid Profile or Cancer Marker Test today at your nearest Manipal TRUtest center and take a proactive step toward safeguarding your health.
Thyroid
Know Your TSH, T3, and T4 Levels with a Thyroid Profile Test
The thyroid gland, though small in size, plays a vital role in regulating numerous bodily functions. Located at the base of your neck, this butterfly-shaped gland produces hormones that influence your metabolism, energy levels, heart rate, mood, and overall well-being. An imbalance in thyroid hormones can cause significant health issues, making it essential to monitor their levels regularly. A Thyroid Profile Test is the most effective way to assess the functioning of your thyroid gland by measuring the levels of TSH, T3, and T4 in your blood.
Understanding the Three Key Components
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
TSH is produced by the pituitary gland and acts as a messenger to the thyroid gland, instructing it to produce T3 and T4. Elevated TSH levels often indicate hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), while low levels may suggest hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
- Triiodothyronine (T3)
T3 is the active thyroid hormone that helps regulate metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate. Abnormal T3 levels can result in symptoms like weight fluctuations, irregular heartbeat, and mood changes.
- Thyroxine(T4)
T4 is the primary hormone produced by the thyroid gland, later converted into T3 in the body. It plays a crucial role in maintaining metabolism, digestion, and brain development. Imbalances in T4 levels can affect your physical and mental health.
Why a Thyroid Profile Test is Important
Thyroid disorders often develop gradually and may remain unnoticed until symptoms become severe. Common signs of thyroid imbalance include fatigue, weight gain or loss, hair fall, anxiety, depression, irregular menstrual cycles, and difficulty concentrating. Since these symptoms can be mistaken for other health conditions, a Thyroid Profile Test helps in early detection and accurate diagnosis.
Who Should Get Tested?
You should consider a Thyroid Profile Test if you:
- Experience persistent fatigue, mood swings, or unexplained weight changes.
- Have a family history of thyroid disorders.
- Is pregnant or planning pregnancy, as thyroid health impacts fetal development.
- Have symptoms like hair thinning, swelling in the neck, or irregular heartbeats.
How the Test Works
The procedure is simple and involves a standard blood sample collection. The blood is analyzed to measure the levels of TSH, T3, and T4, and the results help your doctor determine whether your thyroid is functioning normally, underactive, or overactive.
Benefits of Regular Thyroid Testing
- Early Detection – Identifies thyroid problems before they worsen.
- Personalized Treatment – Helps your doctor tailor the right medication and dosage.
- Prevention of Complications – Untreated thyroid disorders can lead to heart disease, infertility, or severe metabolic issues.
- Better Quality of Life – Managing thyroid hormone levels can restore energy, improve mood, and stabilize weight.
At Manipal TRUtest, we offer accurate Thyroid Profile Tests that measure TSH, T3, and T4 levels to provide a clear understanding of your thyroid health. With NABL-accredited labs, doorstep sample collection, and quick digital reports, managing your thyroid has never been easier.
Don’t ignore the signs of thyroid imbalance. Book your Thyroid Profile Test with Manipal TRUtest today and take control of your health.
Thyroid
Why Regular Thyroid Testing is Important for Women
Thyroid testing is crucial for women as thyroid disorders often go unnoticed but can significantly impact metabolism, mood, menstrual health, fertility, and overall well-being. Early detection through testing helps manage conditions like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism effectively, ensuring hormonal balance and better long-term health outcomes for women of all ages. It produces hormones that control metabolism, energy levels, heart rate, body temperature, and menstrual cycles. For women, thyroid health is especially crucial due to its close link with hormonal balance, reproductive health, and overall well-being. Regular thyroid testing helps detect any dysfunction early, enabling timely management and prevention of serious complications.
The Impact of Thyroid Disorders on Women
Women are five to eight times more likely than men to suffer from thyroid problems, making them a high-risk group. The most common thyroid disorders are hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid). Both conditions can disrupt daily life significantly if left undiagnosed or untreated. Symptoms such as fatigue, unexplained weight gain or loss, hair thinning, irregular periods, mood swings, and infertility can often be attributed to thyroid imbalances.
In particular, Hypothyroidism is more prevalent among women, especially those over 30 or during life stages like pregnancy and menopause. If not managed properly, it can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease, goitre, or complications during pregnancy. Hyperthyroidism, though less common, can also cause anxiety, rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and sleep disturbances.
Hormonal Health and Fertility
Thyroid hormones are deeply interlinked with the reproductive system. Women with untreated thyroid disorders may experience menstrual irregularities, difficulty conceiving, or even recurrent miscarriages. A healthy thyroid is essential for maintaining regular ovulation and supporting pregnancy. This is why endocrinologists often recommend thyroid screening as part of preconception and prenatal check-ups. An undiagnosed thyroid issue can quietly hinder fertility, making regular testing crucial for women planning a family.
Thyroid Testing: What It Involves
Thyroid function is primarily assessed through a simple blood test that measures Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) levels, along with T3 and T4 hormones. In some cases, additional tests for thyroid antibodies may be required to detect autoimmune thyroid disorders like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease. These tests are quick, affordable, and highly effective in identifying imbalances before symptoms become severe.
Early Detection Better Health Outcomes
The major benefit of regular thyroid testing is early detection. Many thyroid disorders develop gradually and remain unnoticed until they cause significant health deterioration. By scheduling regular check-ups especially for women with a family history of thyroid issues, diabetes, or autoimmune conditions it is possible to diagnose the problem early and begin appropriate treatment. This may include hormone replacement therapy, lifestyle changes, or medications to regulate hormone production.
When Should Women Get Tested?
Experts suggest that women over the age of 30 should undergo a thyroid screening every five years, or more frequently if symptoms arise. Pregnant women, those planning to conceive, or women with irregular menstrual cycles, mood changes, or unexplained weight fluctuations should not delay testing.
Thyroid health is a silent cornerstone of a woman’s overall well-being. Regular thyroid testing empowers women to take charge of their health, ensuring hormonal balance, fertility, mental clarity, and energy levels are all maintained. Ignoring thyroid issues can lead to long-term health complications, but with timely diagnosis and treatment, they can be effectively managed. Prioritizing regular thyroid screening is not just a medical necessity it is a proactive step towards a healthier, more balanced life.
Stay proactive. Stay balanced. Get tested.
