Book on Whatsapp
9892101616
Staying Healthy During Monsoon: Recognizing Symptoms
Monsoon Fever
Thu Jul 06 2023
As the monsoon season brings relief from the scorching heat, it also presents various health challenges. Monsoon viral infections, such as swine flu, malaria, dengue, and chikungunya, can spread rapidly during this time. In this blog post, we will explore the common symptoms of these infections and provide essential tips to stay healthy and protect yourself during the monsoon season.
Swine Flu: Swine flu, also known as H1N1 influenza, is a respiratory disease caused by the Influenza A Virus. Symptoms of swine flu include high fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, headache, and fatigue. In severe cases, it can lead to complications such as Pneumonia. To prevent swine flu, maintain good hygiene practices like regular handwashing, covering your mouth while coughing or sneezing, and getting vaccinated if recommended by healthcare professionals.
Malaria: Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease caused by the Plasmodium parasite. Symptoms of malaria include Fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue. It is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms, as early detection can lead to prompt treatment and prevent complications. To prevent malaria, use mosquito repellents, sleep under mosquito nets, and eliminate stagnant water breeding grounds around your living area.
Dengue: Dengue is a viral disease transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes. Symptoms of dengue include high fever, severe headache, joint and muscle pain, rash, and fatigue. In severe cases, dengue can lead to dengue haemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome, which can be life-threatening. To prevent dengue, eliminate stagnant water, wear protective clothing, and use mosquito repellents. Seek medical attention if you suspect dengue symptoms.
Chikungunya: Chikungunya is a viral infection transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes. Symptoms include high fever, joint pain, headache, muscle pain, and rash. Chikungunya can cause long-term joint pain and stiffness. To prevent chikungunya, follow mosquito control measures, wear protective clothing, and use mosquito repellents. If you experience symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
Monsoon Viral Infections: Apart from specific diseases, monsoon season can also lead to various respiratory and gastrointestinal infections. Symptoms may include cough, cold, sore throat, fever, diarrhea, and vomiting. To stay healthy, maintain good personal hygiene, drink clean and boiled water, consume freshly prepared food, and avoid street food or unhygienic eating establishments.
Tips to Stay Healthy During Monsoon:
· Maintain good personal hygiene, including regular handwashing with soap and water.
· Keep your living environment clean and free from stagnant water.
· Drink clean and boiled water to avoid waterborne infections.
· Consume fresh, hygienically prepared food to prevent foodborne illnesses.
· Avoid walking through waterlogged areas to prevent contact with contaminated water.
· Wear appropriate clothing, such as long sleeves and pants, to protect yourself from mosquito bites.
· Use mosquito repellents and mosquito nets while sleeping.
· Stay updated with vaccinations, including flu shots and recommended vaccines for specific diseases.
· Seek medical attention if you experience persistent symptoms or suspect any infections.
Conclusion: As the monsoon season arrives, it's crucial to be aware of the symptoms of viral infections like swine flu, malaria, dengue, and chikungunya. By recognizing these symptoms early on, you can seek timely medical help and prevent complications. Additionally,
Related Blogs
Monsoon Fever
Post-Monsoon Infections: Why Dengue, Malaria, and Typhoid Blood Tests Are Still Essential in November
The monsoon season brings much-needed relief from the summer heat, but it also creates the perfect environment for several infectious diseases. Even after the rains end, the risk of infections like dengue, malaria, and typhoid remains high. November is a critical month when stagnant water, humid weather, and fluctuating temperatures continue to support the growth of mosquitoes and bacteria. This makes timely blood tests essential for detecting infections early and preventing complications.
Why the Risk Persists After Monsoon
Many people assume that the end of the rainy season marks the end of mosquito-borne and waterborne diseases. However, that is not the case. Stagnant water in open containers, drains, and puddles remains a breeding ground for mosquitoes long after the rains stop. Mosquitoes carrying the dengue and malaria parasites thrive in this environment. Similarly, contaminated water and poor hygiene during the post-monsoon period increase the risk of typhoid and other gastrointestinal infections.
Dengue: Early Detection Matters
Dengue fever is caused by the bite of the Aedes aegypti mosquito. Symptoms often include high fever, body pain, rashes, and nausea. In severe cases, it can progress to dengue hemorrhagic fever, which may lead to internal bleeding and organ damage. A simple blood test, such as the dengue NS1 antigen test or antibody test, helps in quick diagnosis. Early detection is critical because dengue does not have a specific cure, and supportive care works best when started at the right time.
Malaria: A Preventable Yet Persistent Threat
Malaria remains one of the most common post-monsoon infections. It is transmitted by the bite of the female Anopheles mosquito. Symptoms include chills, sweating, fatigue, and recurring fever. If untreated, malaria can cause severe anemia, kidney damage, and other complications. A malaria blood test, such as a peripheral smear or rapid antigen test, confirms the presence of the parasite. Testing is important even if symptoms seem mild, as malaria can quickly worsen without proper treatment.
Typhoid: The Hidden Post-Monsoon Danger
Unlike mosquito-borne diseases, typhoid is spread through contaminated water and food. During November, water stagnation and unhygienic conditions make it easier for the Salmonella typhi bacteria to infect people. Typhoid presents with symptoms like prolonged fever, stomach pain, weakness, and loss of appetite. A Widal test or blood culture can confirm the infection. Timely diagnosis helps in prescribing the right antibiotics and preventing serious complications such as intestinal perforation.
Importance of Blood Tests in November
Post-monsoon illnesses often mimic each other, making self-diagnosis difficult. Fever, fatigue, and body aches can be common to dengue, malaria, or typhoid. Without blood tests, accurate treatment is delayed, which increases the risk of complications. Doctors rely on these tests to confirm the exact cause of illness and to begin the right course of treatment quickly.
Prevention Is the First Step to Protection
Along with regular testing, following preventive measures can greatly reduce your risk:
- Avoid stagnant water around your home.
- Use mosquito repellents and nets.
- Drink clean, boiled, or filtered water.
- Eat home-cooked meals and maintain good hygiene.
- Strengthen your immunity through a balanced diet, fruits, and adequate rest.
By staying alert and proactive, you can prevent infection before it disrupts your health or festive plans.
Stay Protected with Manipal TRUtest
The end of monsoon doesn’t mean the end of infections. November remains a sensitive time for dengue, malaria, and typhoid. A simple post-monsoon blood test can make all the difference in protecting your health.
At Manipal TRUtest, we offer comprehensive fever and infection panels that help detect seasonal illnesses accurately and at the earliest stage.
✅ Book your test today and step into the festive season with confidence and care.
Because your health deserves attention — not assumptions.

Monsoon Fever
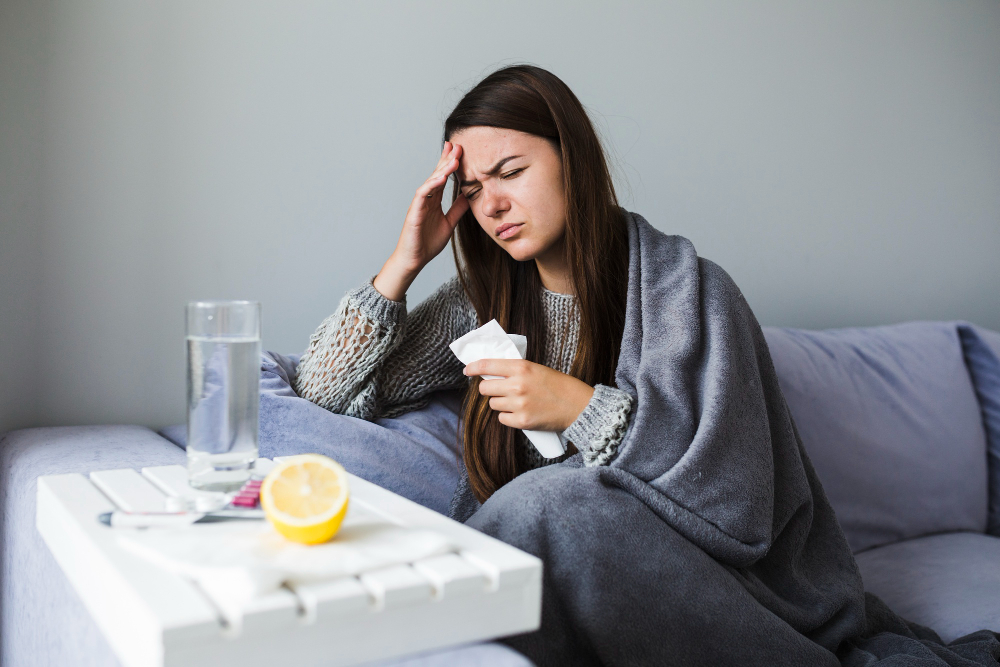
When Fever Persists, Get Tested for Better Health
A fever is the body’s natural response to infections, signaling that the immune system is actively fighting off viruses or bacteria. However, when a fever lasts more than 3 days or keeps recurring, it’s essential to take it seriously. In such cases, a fever test can help identify the underlying cause—whether it’s a viral infection, bacterial illness, or something more serious. Ignoring prolonged or repeated fevers may delay the diagnosis of deeper health conditions. A timely fever test ensures early detection and proper treatment, safeguarding your long-term health.
In some cases, a prolonged fever may also indicate a serious bacterial infection, such as typhoid, tuberculosis, or a urinary tract infection. It could also be associated with conditions like malaria, autoimmune disorders, or even certain types of cancers. If left untreated, these underlying issues may worsen over time.
Warning Signs That Require Attention
If a fever lasts more than a few days and is accompanied by chills, night sweats, loss of appetite, fatigue, or unexplained weight loss should not be overlooked.
These symptoms require immediate medical attention. Diagnostic tools like
blood tests, imaging scans, or cultures can help identify the exact cause.
The causes of prolonged fever range from common viral infections like dengue, malaria, and flu to more serious conditions such as tuberculosis, urinary tract infections, or autoimmune disorders. In some cases, persistent fever may even point toward cancers like leukemia or lymphoma. Instead of relying solely on home remedies or over-the-counter medicines, consulting a healthcare professional and getting tested is essential.
Importance of Diagnostic Testing
Diagnostic tests such as a complete blood count (CBC), malaria parasite test, dengue NS1 antigen, urine analysis, and chest X-ray can help identify the exact cause. Blood cultures and other advanced investigations may be necessary if the fever remains unexplained. These tests not only detect infections but also evaluate the functioning of key organs like the liver and kidneys.
Delaying diagnosis can make the illness worse. For instance, in typhoid or urinary infections, untreated fever can lead to severe complications. In cases like tuberculosis or viral hepatitis, early detection through testing can prevent transmission to others and ensure timely treatment.
Risks of Delaying Diagnosis
Moreover, persistent fever may affect energy levels, appetite, and sleep, weakening the immune system further. Children, the elderly, and people with chronic conditions are more vulnerable to the risks associated with high or prolonged fever.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fever should never be taken lightly, especially if it lasts beyond a few days. Instead of waiting for it to resolve on its own, timely testing and diagnosis can lead to better outcomes. Being proactive with your health not only speeds up recovery but also helps in preventing complications and safeguarding others around you.

Monsoon Fever
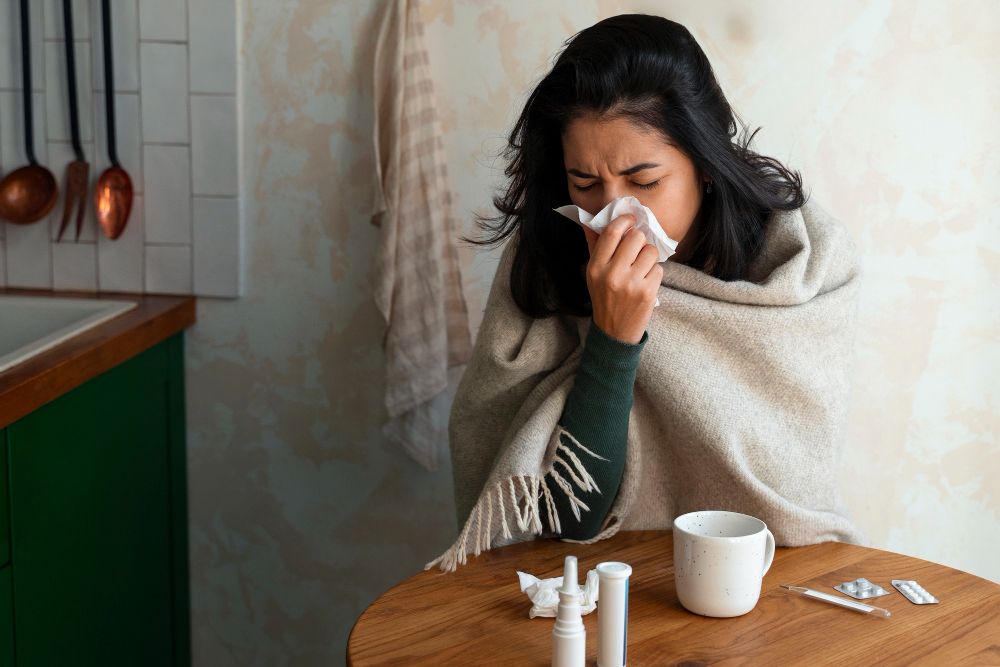
Different Types of Seasonal Infections and How to Prevent Them
Seasonal changes bring beautiful weather shifts but they also invite a host (lot) of infections. Whether it's monsoon, winter, or summer, each season has its own set of common illnesses. Knowing about these infections and how to protect yourself can help you stay healthy throughout the year.
Common Seasonal Infections
1. Flu and Cold
The flu and cold are classic examples of infections that peak during the winter months. They are caused by viruses and spread easily from person to person through coughs, sneezes, and contaminated surfaces. Symptoms usually include sore throat, cough, fever, and body aches.
2. Dengue and Malaria
During the rainy season, mosquito-borne diseases like dengue and malaria become widespread. Stagnant water provides a breeding ground for mosquitoes, making it easier for these infections to spread.
3. Gastrointestinal Infections
Hot and humid summers can lead to food and waterborne diseases such as diarrhoea, food poisoning, and cholera. Eating contaminated food or drinking unsafe water increases the risk significantly.
4. Respiratory Infections
Respiratory infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia are more common during winter. Dust, pollution, and dry air can worsen breathing problems, especially for people with asthma.
5. Skin Infections
Fungal infections, rashes, and other skin problems tend to rise during the monsoon season due to increased humidity. Wet clothes and damp skin create the perfect environment for infections to grow.
How to Prevent Seasonal Infections
Maintain Good Hygiene
Washing your hands regularly with soap and water can prevent many infections. Always clean your hands before eating and after using the restroom. Carry a sanitizer when water isn’t available.
Boost Your Immunity
A strong immune system is your best defence. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and proteins can strengthen your immunity. Adequate sleep, regular exercise, and staying hydrated also play important roles.
Avoid Mosquito Bites
Use mosquito repellents, wear long-sleeved clothes, and keep your surroundings clean. Make sure there is no stagnant water near your home, as this can be a breeding site for mosquitoes.
Stay Updated with Vaccinations
Certain infections, like the flu, can be prevented with timely vaccination. Consult your doctor about vaccines, especially before the start of flu season.
Eat Fresh and Clean Food
During summers and rainy seasons, ensure that the food you consume is freshly cooked and properly stored. Avoid eating from roadside vendors, as it may increase your risk of food poisoning.
Seek Early Medical Advice
If you experience symptoms like high fever, body aches, vomiting, or persistent cough, do not ignore them. Early diagnosis can prevent complications. You can book health check-ups conveniently through trusted platforms like manipaltrutest.com.
Seasonal infections are common, but they can often be avoided with simple precautions. Maintaining hygiene, eating healthy, preventing mosquito bites, and seeking timely medical help are key steps toward a healthy life.
Stay aware of the infections each season brings, and take proactive measures to protect yourself. For easy access to diagnostic services and health tests, visit manipaltrutest.com and stay a step ahead of seasonal illnesses.
